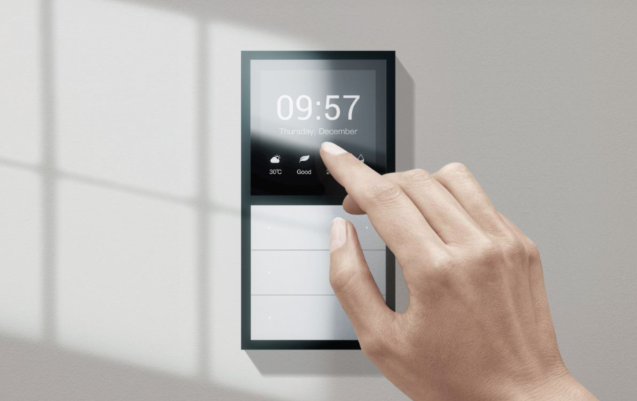
LCDs (liquid crystal displays) are flat-panel displays that use electrically charged liquid crystals to control the amount of light passing through them. They are commonly used in devices such as TVs, smartphones, laptops, digital cameras, and gaming systems. Touch panels, on the other hand, are user interfaces that allow users to interact with devices by touching screens or surfaces that recognize their inputs. Touch panels are often combined with LCDs to create touchscreens, which are increasingly prevalent in today's devices.
Both LCDs and touch panels have been widely adopted due to their many benefits over alternative technologies. For instance, LCDs are lightweight, thin, and energy-efficient, making them ideal for mobile devices. They also have high color saturation and contrast, making them suitable for displaying high-quality images and video content. Additionally, LCDs have a longer lifespan than CRT (cathode ray tube) displays and are more environmentally friendly as they do not contain hazardous components.
Touch panels, on the other hand, enable intuitive and interactive user interfaces that enhance user experience and simplify device control. They are particularly useful for display devices such as smartphones, tablets, and car infotainment systems, as they enable users to interact with devices using natural gestures such as swipes and taps. Touch panels also provide better accuracy, speed, and responsiveness than traditional input devices such as keyboards and mice.
The suitability of LCD and touch panels in various applications depends on the specific requirements of those applications. For instance, in the healthcare industry, LCD touchscreens are becoming increasingly popular for use in medical monitors and mobile devices used by doctors and nurses. The touchscreen interface allows them to quickly access and update patient records, view medical images, and adjust equipment settings.
Another application where touchscreens are increasingly popular is in the automotive industry, where they offer improved safety and convenience. For example, touchscreens embedded in cars' dashboards can provide easy access to multimedia content or help drivers locate nearby gas stations. In-cabin touchscreens can also be used to control the vehicle's temperature, lighting, and other features, reducing the need for manual controls that can be distracting while driving.
In the gaming industry, LCDs and touchscreens are widely used for handheld devices such as portable game consoles and smartphones. Their ability to display high-quality graphics and precise touch inputs enhances the gaming experience and creates a more immersive environment for gamers. Additionally, touch panels can be used in arcade-style games, providing players with a unique and intuitive way to interact with the game.
One of the challenges with LCD and touch panels is their susceptibility to damage from external factors such as water, temperature, and physical impact. This issue can be particularly significant in military and industrial applications where devices are exposed to harsh environments. However, industry leaders have been working to develop LCD and touch panels that are more resilient and reliable. For example, some devices now come with IP67 or higher ratings, indicating that they can withstand dust, water, and other environmental hazards.
In conclusion, LCD and touch panels are suitable for a wide range of applications across industries, including healthcare, automotive, gaming, and many others. These technologies offer numerous benefits, including high image quality, energy efficiency, and improved user experience. While they are prone to damage from external factors, advancements in technology have created solutions that make them more durable and reliable. With ongoing innovation, LCD and touch panels are expected to continue advancing, leading to new and improved use cases in the future.